Since the antenna as well as the RF circuit is placed above the solar cell, a high optical transparency is desired in order not to decrease the efficiency of the solar cell significantly. First, an optically transparent carrier material is needed. In this case, quartz glass is best suited since it has good optical characteristics as well as dielectric properties.
In terms of optically transparent and conductive materials, there are many possibilities to realize transparent conductive strip lines. Nowadays, optically transparent conductive materials are widely used in applications such as photovoltaics, displays and touch screens. Frequently used materials for antennas are Transparent Conducting Oxides (TCOs) such as Indium Tin Oxide (ITO), Silver Nanowires (AgNWs) or meshed grid lines made of conventional metal layers. Our investigation and other research works showed that metal grid lines are best suited for the realization of RF structures.
A study of the changes in antenna performance caused by meshing of the patch antenna as well as the ground plane was carried out [1]. Hereby, the operating frequency is 24 GHz. The results showed that applying the meshing method on the patch a lower resonance frequency can be achieved resulting in smaller dimensions for a given frequency. At the same time, the corresponding bandwidth and peak gain values are reduced. These effects are less dominant when the density of the grid gets higher at the same transparency (increasing the number of lines thus decreasing the line width). Decreasing the lines where the current density is high has a higher impact on resonance frequency and bandwidth.
Based on the investigated geometry meshing the ground plane gives the possibility to enhance the bandwidth from 1.2 % (solid ground) to 3.5 %.
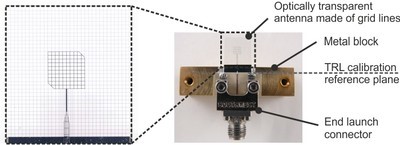
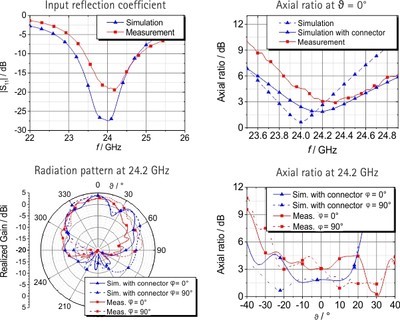
In order to ensure a proper communication link between the communication module and a reader unit regardless of the orientation of the antenna, a circularly polarized patch antenna was investigated [2]. The antenna consisting of grid lines is studied concerning the impedance behavior due to the applied mesh. A single fed truncated corners meshed patch antenna with meshed ground plane on quartz glass is investigated (see Fig. 1). The simulation and measurement results are depicted in Fig. 2. The proposed antenna has an optical transparency of 92 %, an input reflection coefficient of -27 dB and a minimum axial ratio of 0.6 dB at 24 GHz as well as a simulated realized gain value of 4 dBi in the main direction. The radiation efficiency is 43 % (opaque counterpart 85 %).




Referenzen
[1] Q.H. Dao, R. Braun, B. Geck, Design and Investigation of Meshed Patch Antennas for Applications at 24 GHz, in: European Microwave Conference 2015, Paris, France, 2015.
[2] Q.H. Dao, T. Cherogony, B. Geck, Optically Transparent and Circularly Polarized Patch Antenna for K-Band Applications, in: 10th German Microwave Conference, GeMiC 2016, Bochum, Germany, 2016.


